The “Tianyu” orthopedic surgery robot is full of industrial atmosphere. Under its strong appearance, it is composed of countless high-precision components.
Compared with human beings, Tianyi surgery robot has a more stable and accurate control ability, which means smaller wounds, faster recovery speed and safer operation procedures for patients, which can minimize the pain caused by surgery.
With so many advantages, does it mean that doctors may face unemployment as surgical robots develop? To what extent has “robot” technology developed in the medical field? What will the future look like? Is there a security problem? As ordinary patients, should we actively embrace new technologies or should we be critical to observe carefully?
According to Frost & Sullivan, the global surgical robot market increased from 3 billion US dollars to 8.32 billion US dollars from 2015 to 2020, with a compound growth rate of 22.6%, of which the Chinese surgical robot market increased from US$93 million to 4.2 million. 500 billion US dollars (about 2.76 billion yuan), with a compound growth rate of 35.7%, is estimated that by 2026, the global market will reach 33.59 billion US dollars, and the Chinese market will reach 3.84 billion US dollars (about 25 billion US dollars), with a compound growth rate of 44.3%, representing a global market share from 5.1% in 2020. It rose to 11.4%.
The orthopedic surgery robot industry rose in 2015. The global orthopedic surgery robot market reached 1.39 billion US dollars in 2020. According to Frost & Sullivan’s forecast, it is expected to reach 4.69 billion US dollars in 2026, which will become the next wide range after endoscopic surgical robots. In the field of ubiquation, and at present, orthopaedic surgery robots are on the eve of the blooming market application.
Tianzhihang: the first self-developed localized orthopedic surgery robot
Tianzhihang entered the field of orthopedic robots early. According to Dr. Xu Jin, general manager, Tianzhihang was established in 2005 and focused on orthopedic surgical robots from the beginning. At that time, surgical robot was still a relatively strange concept. The reason why orthopaedics was chosen as the entry point was to focus on the development prospects of the orthopedic market. Through intelligent robots to assist doctors, the whole orthopaedic surgery process could be optimized to make the operation more accurate and the wound smaller.
At the same time, Tianzhihang also chose medical and scientific research institutions such as Beijing Jishuitan Hospital and Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics as partners. On the one hand, it can obtain the most cutting-edge clinical information, and on the other hand, it can be deeply cultivated in mechanical control and other fields.
Unlike the reverse development idea of most products, the development of “Tianyi” orthopedic surgery robots is a positive development from an Idea. In continuous communication with doctors, obtain clinical needs and use it to build the original prototype. It is also relying on this development idea that Tianzhihang independently developed China’s first surgical robot that has obtained a CFDA registration certificate.
surgery robot Insurmountable “1mm” moat
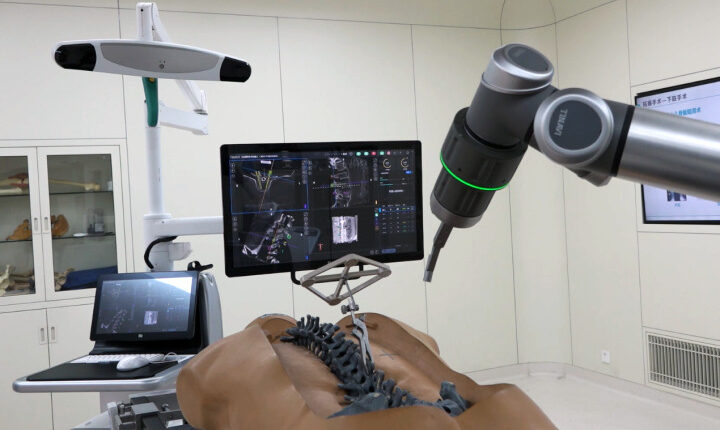
Some patients joked after surgery, “I thought the surgical robot was a personal machine to operate on me!” In fact, many patients have such a misunderstanding. In fact, the current “Tianyi” orthopedic surgery robot is more like an auxiliary tool for doctors. Through the guidance of the robot arm, it solves the problem of “invisibility, inaccurate and unstable” of traditional orthopedic surgery.
In traditional orthopedic surgery robot, deep incisions are usually caused, and doctors must perform multiple, multi-angle X-rays to the patient’s surgical site to confirm whether the position of orthopedic implants entering the human body conforms to the surgical plan, which exposes patients and doctors to radiation for a long time. The “Tianyi” orthopedic surgery robot can replace the traditional diagnosis and treatment method through positioning and calculation.
Although it is assisted by robots, the operation is still dominated by doctors. Doctors first need to scan the patient by X-ray and transmit the scanning data to the “bot”. At this time, the doctor can realize “visualization” operation through the robot’s console. After formulating the surgical planning route, there is no need to carry out multiple X-rays. The “robot” can help doctors accurately locate the surgical position and control the direction and angle of the guide needle according to patient data and surgical planning, through its own multiple sensors and complex calculations.
This process is like a target in a “black” box. Doctors can’t directly see the bull’s eye, but the “robot” can not only find the bull’s eye, but also assist the doctor to aim. More importantly, even if the position of the bull’s eye changes, the “robot” can still automatically again according to the change of position. Adjust to achieve real-time aiming and control the accuracy within 1mm. With the help of the “robot”, doctors only need to “pulse the trigger” to hit the bull’s eye accurately. This process is a crucial link in orthopedic surgery. The accuracy of positioning directly determines the smoothness and quality of the doctor in the follow-up operation.
The seemingly inconspicuous “1mm”, Tianzhihang surgery robot research and development team has experienced countless setbacks. At first, the robot can only achieve a positioning accuracy of 2mm. In order to complete the leap from 2mm to 1mm, the whole team keeps pushing back. After experiencing countless technical improvements and re-verification, it is clear that the technology has achieved the expected effect, but because the processing or measurement link is not in place, it has experienced nothing.
Several times of product polishing, finally a mature and stable product was launched. Generally, ordinary clinical trials are only about half a year at most, while the clinical stage of the “Tianyi” orthopedic surgical robot has gone through up to a year and a half. It is precisely because of this 1mm accuracy that the “Tianyu” orthopedic surgery robot has completed the comprehensive coverage from the upper cervical vertebrae to the spinal surgery, and has become an insurmountable moat.
According to Dr. Xu Jin, traditional pelvic surgery robot may require a large incision of more than 30 centimeters, bleeding more than 3,000ml during the operation, and it takes about 2-3 months to walk on the ground after surgery. With the use of the “Tianyi” orthopedic surgery robot, the bleeding volume can generally be controlled at about 20ml, and two or three screws can solve the operation. Patients can basically walk on the ground 1-2 days after surgery, so the progress of this technology can bring huge benefits to both doctors and patients.
Surgical robots will prolong the career of doctors.
In any country, doctors are a scarce resource, and for doctors in many departments, the golden cycle of their careers is shorter than expected. Especially for orthopedic surgeons, the real golden cycle is only about ten years.
From medical school to work, young doctors have to start with basic surgery and gradually grow up until they can master more complex operations. This requires a lot of experience and is a long process. After the age of 50, orthopedic surgeons often start to decline. With the degradation of eye and muscle function, some minimally invasive and difficult operations will become more and more difficult for them to do.
Until the emergence of surgical robots greatly improved the development speed and life cycle of doctors’ careers. For young doctors, surgical robots improve the speed of doctors’ learning, and assist some key steps in the operation by surgical robots, thus shortening the time that requires repeated practice to master skills. For older doctors, surgical robots make up for the shortcomings caused by the degradation of eye and muscle functions, which can greatly prolong the professional life cycle of doctors.
How does the surgical robot ensure safety?
Many patients will have concerns about the safety of surgical robots. According to media reports, in February 2015, the first robot heart valve repair surgery in the United Kingdom splashed blood, and finally failed. The results of the later hearing survey showed that the more reason behind the tragedy was that the surgeon was not fully prepared for the operation and did not fully master how to operate the machine.
However, the two medical robot experts who should be at the scene failed to appear at the time of the accident, resulting in the master knife inability. Get effective help.
Regarding the safety considerations and design of the “Tianyu” orthopedic surgical robot, Dr. Xu Jin said, “Based on the awe of life, we have a complete research and development system.” When the orthopedic surgery robot was set up, it had put safety first.
At present, the positioning of the orthopedic surgery robot of Tianyi is to assist doctors in auxiliary work. All surgical decisions on the scene are controlled by doctors. The operation of each key step of the robot is also reviewed and approved by a doctor.
At the beginning of the design, the product has fully considered the possible emergencies in various links, including ensuring that there is no major medical accidents in the event of power outages or core component failure. At the same time, in order to ensure the standardized operation of doctors, a three-day mandatory training has also been set up to ensure that doctors can operate accurately in all links.
On this basis, when the doctor returns to the hospital to carry out the operation, there will also be special clinical engineers and experts to guide the follow-up surgery, and the number of follow-up operations will be guaranteed to be at least 30-50 until the doctor fully masters the operation points of the “Tianyi” orthopedic surgery robot.
The internationally renowned academic journal Science Robotics (ScienceRobotics) defines the degree of automation of medical robots and is divided into six stages, namely, no automation (Phase I), Robotics (Phase II), Task Automation (Phase III), Conditions Automation (Phase IV), High Automation (Phase V), Full Automation (Phase VI).
Dr. Xu Jin also mentioned Tian Zhihang’s vision of future surgical robots, but it did not think according to the “six stages” of academic journals, but more like a natural growth process.
He mentioned that the surgery robot is an iterative cycle about every 3-4 years. The indications of each generation of products are broader, and the degree of automation and intelligence will be higher. The core is to build a highly integrated operation platform around patients.
At present, the proportion of doctoral and graduate students in Tianzhihang’s research and development team has reached 40%. As of June 30, 2021, 171 patents have been granted (including 36 invention patent authorizations). In the first half of this year alone, 17 new patent applications (including 6 applications for invention patents) were filed.
It can be seen that Tianzhihang is in the stage of rapid development at this time, and the reason for this speed is that in their R&D team, there is a distinctive R&D team, which is mainly responsible for exploring new technologies or products that may appear in the next 5-10 years, which are characterized by agility, rapidity and boundless The world can be developed in the air, combined with the characteristics of small and fast, make various prototypes, and constantly look for possible future development trends.
Perhaps it is precisely because of such a “front-edge commando team” that the “Tianyi” orthopedic surgery robot has maintained an industry leading edge in the field of orthopaedic positioning and navigation for many years.
Perhaps because it entered the industry earlier, Tianzhihang currently has a market share of nearly 80% in the field of orthopedic surgery robots. But in the future, as more and more enterprises enter this field, the competition will also intensify. As for the ultimate form of the future surgical robot, no one can say clearly, but in the direction, it will certainly develop in the direction of higher and higher accuracy, integration and security. Perhaps one day in the future, the fully automatic medical warehouse in science fiction will eventually be brought into reality.